Fiber optic cable is a type of telecommunication cable made from glass or plastic, which transmits signals using light. This cable plays a crucial role in providing stable signal transmission at the highest speeds. Unlike copper cables that transmit signals via electricity and are prone to interference, fiber optic cables have minimal interference and offer higher speeds, transmitting signals over longer distances.
If you’re unsure which fiber optic cable to choose based on quality, type, or model, NT Security is here to clear up your questions and provide information on the most widely used fiber optic cable types available on the market today.
Types of Fiber Optic Cables on the Market
Despite its very small size, comparable to a human hair, fiber optic cable offers numerous benefits. It caters to users’ needs by supporting higher bandwidth and faster signal transmission. Large corporate networks as well as small office networks run efficiently due to fiber optic transmission, saving both time and costs during operations.
Currently, the market offers two main types of fiber optic cables: Multimode and Single mode.
- Multimode Fiber Optic Cables: These have a larger core diameter (50µm or 62.5µm), allowing light to travel in multiple paths. These fibers can transmit multiple wavelengths simultaneously, depending on the cable’s specifications. The most commonly used multimode cables are OM2 and OM3, available in both indoor and outdoor standards.
- Single Mode Fiber Optic Cables: These have a smaller core diameter (8µm or smaller), with less refraction between the core and cladding compared to multimode fibers. Single Mode fibers transmit only one light path parallel to the axis. Common types of single mode fiber cables include aerial cables, direct burial cables, and duct cables, each suited for different installation scenarios.

Most Common Fiber Optic Cable Types Used on the Market
Fiber optic cables are now widespread and available in a variety of models and types, such as tight-buffered cables, duct cables, and direct burial cables. Each type suits different installation environments and has unique characteristics, specifications, and standard designs.
- FTTH (Fiber to the Home) Cables: Also known as subscriber optical cables, these are used primarily by ISPs for delivering internet services. FTTH cables typically come in 1FO, 2FO, and 4FO variants and are designed for home use and small LAN networks.
- Aerial Fiber Optic Cables: Similar to duct cables, but reinforced with a steel strand, forming a figure-eight shape for added flexibility and durability. These cables are commonly seen on utility poles.
- Duct Fiber Optic Cables: These are used for installation in underground ducts. They are typically round and have a hard outer shell, with fiber counts ranging from 4 to 144 fibers. These cables use loose tube technology, allowing the fibers to move freely and preventing damage from environmental stress or rodent activity.

- Direct Burial Fiber Optic Cables: Also known as metal armored duct cables, these are more advanced than standard duct cables, featuring a metallic sheath for protection. They can be buried directly underground or installed in ducts and are resistant to external damage from tools or animals.
- Tactical Fiber Optic Cables: Used mainly in military zones or live broadcast events, these cables are designed to be flexible and mobile, often wound onto a bobbin for easy deployment. They are highly durable against physical impacts.
- ADSS (All-Dielectric Self-Supporting) Cables: Also known as non-metallic aerial cables or long-span cables, ADSS cables are designed to be suspended over long distances between poles, sometimes as far as 100m to 1000m, without sagging or losing durability.
===> Learn more: New and Modern Smart Home Trends: Present and Future
Top 4 Most Commonly Used Fiber Optic Cables
1FO Tight-Buffered Fiber Optic Cable
Also known as 1-core FTTH cable, this small, lightweight fiber cable is ideal for small LAN networks or internal systems like fiber optic-based CCTV setups. It’s easy to transport and install.
2FO Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cable
This 2-core single mode fiber is widely used in FTTH systems, CCTV networks, and internal LANs. With a figure-eight structure and steel reinforcement, it is suitable for both indoor and outdoor installations. The 2FO cable is long-lasting and easier to install than larger tactical, duct, or aerial cables.

4FO Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cable
With four cores, the 4FO cable offers excellent data transmission and features a reflective outer layer made from silica-infused material to prevent solar reflection and interference. Its PVC outer layer is flexible and fire-resistant, making it easy to handle during installation. This cable is commonly used in internal LAN systems or CCTV networks.
8FO Loose Tube Fiber Optic Cable
This cable is designed for long-distance overhead use, commonly seen on power lines or spanning large distances between utility poles. Its HDPE jacket resists physical stress, water, and twisting while offering excellent electrical insulation. It’s ideal for extensive LAN systems or large CCTV networks over long distances.
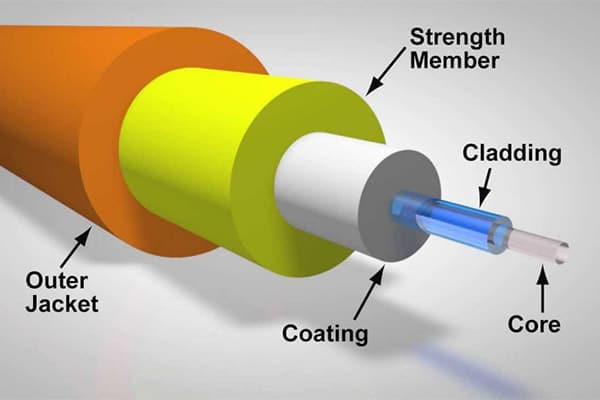
These are the most commonly used fiber optic cables on the market today. If you are looking to install a fiber optic network, feel free to contact NT Security for more information and advice.

